Suppliers
Add your company
Fully Autonomous Multirotor Drones & Hybrid VTOL UAVs With AI Capabilities

Rugged Computing and Video I/O Modules: 6U & 3U VPX, XMC, Small Form Factor and Custom Solutions

Fixed-Wing UAV Systems: Modular VTOL, Long-Range Maritime UAV, Tactical ISR UAS

Inertial Navigation & Positioning Technology for Unmanned, Autonomous Systems

Software-Defined Inertial Navigation Systems (MEMS & FOG), and Acoustic Positioning Solutions

Smart Marine Radar Processing Solutions: Advanced Perception & Situational Awareness for Uncrewed & Autonomous Vessels

Industrial-Grade Embedded Computer Systems for AI Edge Computing & Machine Learning
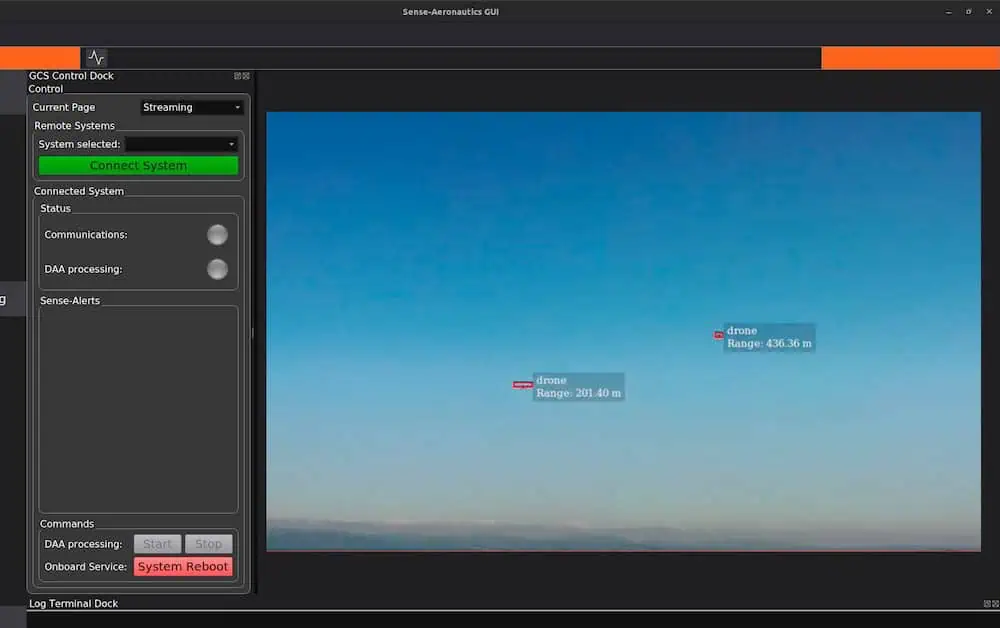
Cutting-Edge AI-powered Drone Video Analytics Solutions for Object Detection

Edge-Based Visual AI Software Platform for Defence & Security Camera Automation

Embedded Systems Software Development, Firmware Programming & Drone Software Design/Testing Services

Underwater Sonar: Side-Scan Imaging Sonar & Forward Looking Sonar for Obstacle Avoidance & Navigation

High-Performance Video Graphics, GPGPU, AI/ML Processing & Display Solutions for C5ISR Applications
If you design, build or supply Artificial Intelligence (AI) Technology, create a profile to showcase your capabilities on this page
Products
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Technology
In this guide
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the ability of machines and robots to perform tasks that would normally require human intelligence, which includes an ability to learn and adapt to changing environments.

Teledyne CARIS’ AI-driven Sonar Noise Classifier
Machine learning is much more complex to develop, compared to rote learning which can be easily implemented on a computer with lists of rules and is comparatively limited and inflexible.
Successful implementation of AI on drones and unmanned vehicles allows the development of self-piloting systems, thus doing away with the need for human operators. This saves manpower and expenses as well as being more efficient for certain tasks that humans cannot perform as quickly as a computer. It may also be one of the keys to unlocking commercial BVLOS (beyond visual line of flight) drone operations at scale.
Applications
UAVs (unmanned aerial vehicles), UGVs (unmanned ground vehicles) and other robotic platforms may use AI for a variety of applications, including;
- Obstacle avoidance
- Swarm operations
- Real-time data analysis and image classification
- Autonomous precision navigation and landing.

Lorenz AI-Link – Artificial Intelligence Computing
AI empowers a drone or robot to make decisions based on inputs from its sensors, and may also allow the vehicle to continue with its mission even when it loses communications with its base of operations.
Artificial Intelligence Components
Key components of AI are machine learning and deep learning software, which allow computers to employ more sophisticated algorithms such as neural networks in order to find patterns and relationships in data. Neural networks need to be trained by providing them with large amounts of example data to learn from. An example of UAV machine learning would be the use of computer vision and sensors to perform the detection, classification and tracking of potential targets.
Embedded AI

Condor NVP2102AxX with GPGPU computing, AI processing, deep learning capabilities by EIZO
AI for drones and robotics can be performed in the cloud or on edge devices, which in the case of unmanned vehicles means onboard computing. Since the data processing occurs close to the source of the data – the onboard sensors – edge devices can allow results to be obtained faster. Hardware options for drone AI edge devices include general-purpose graphics processing units (GPGPUs), central processing units (CPUs), application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs), and systems-on-a-chip (SoCs).
Onboard AI requires a large amount of processing power, which may make edge devices unsuitable for SWaP (size, weight and power)-constrained vehicles. Taking advantage of the cloud for AI processing, however, requires low latency and high bandwidth, which can be difficult to obtain in remote areas and other subpar communications environments. The transmission of data over long distances also poses security and privacy risks.




































