Suppliers
Add your company
Guidance, Navigation & Control Solutions (GNC) for Drones & UAVs

GNSS Receivers & Antennas, Satellite-based PPP Correction Service, and Network RTK Service for Centimeter-level Positioning

Platform-agnostic counter-drone capabilities for fixed & mobile applications

Tactical-Grade Fiber Optic Gyros & FOG IMU for UAVs & Autonomous Vehicles

Certified UAV Communications, Navigation, Control, Surveillance, and Combat ID Solutions

Precise Positioning for Unmanned Vehicles: GPS & GNSS Receivers, Antennas & Inertial Systems

High-Performance GNSS/RTK/GPS PNT Solutions for Drone & Robotics OEMs & Systems Integrators

GNSS Positioning Solutions: RTK GNSS Receivers, UAV Base Stations for Surveying
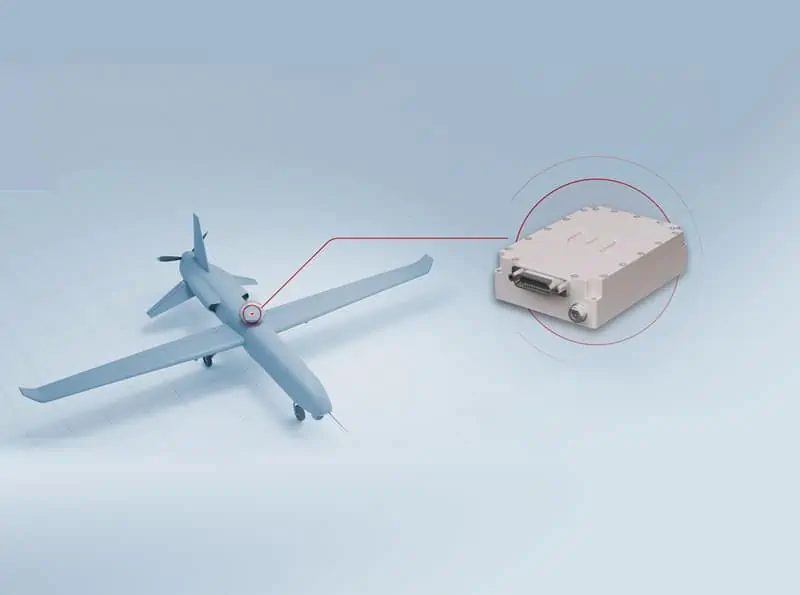
Anti-Jam GPS-GNSS Devices, Tactical Data Links, Telemetry Systems, Electronic Warfare Equipment & Flight Termination Systems

UAV Components: SAR, Radar Altimeter, Data Links, Telemetry, GNSS Products & C-UAS | Tactical USVs

Cutting-Edge Flight Controllers, Sensors, and Other Electronics Technologies for Drones & Robotics

Cost-Effective RTK GNSS Receivers & Antennas for Drones & Robotics

Remote ID & Airspace Awareness Solutions for UAV Pilots, Drone Manufacturers & Law Enforcement Units

GNSS Positioning & Navigation Systems, Mobile Mapping UAV LiDAR & Unmanned Surface Vehicles

Radar & ADS-B Surveillance Data Fusion, Integration & Display | UAV Tracking & ATC Integration
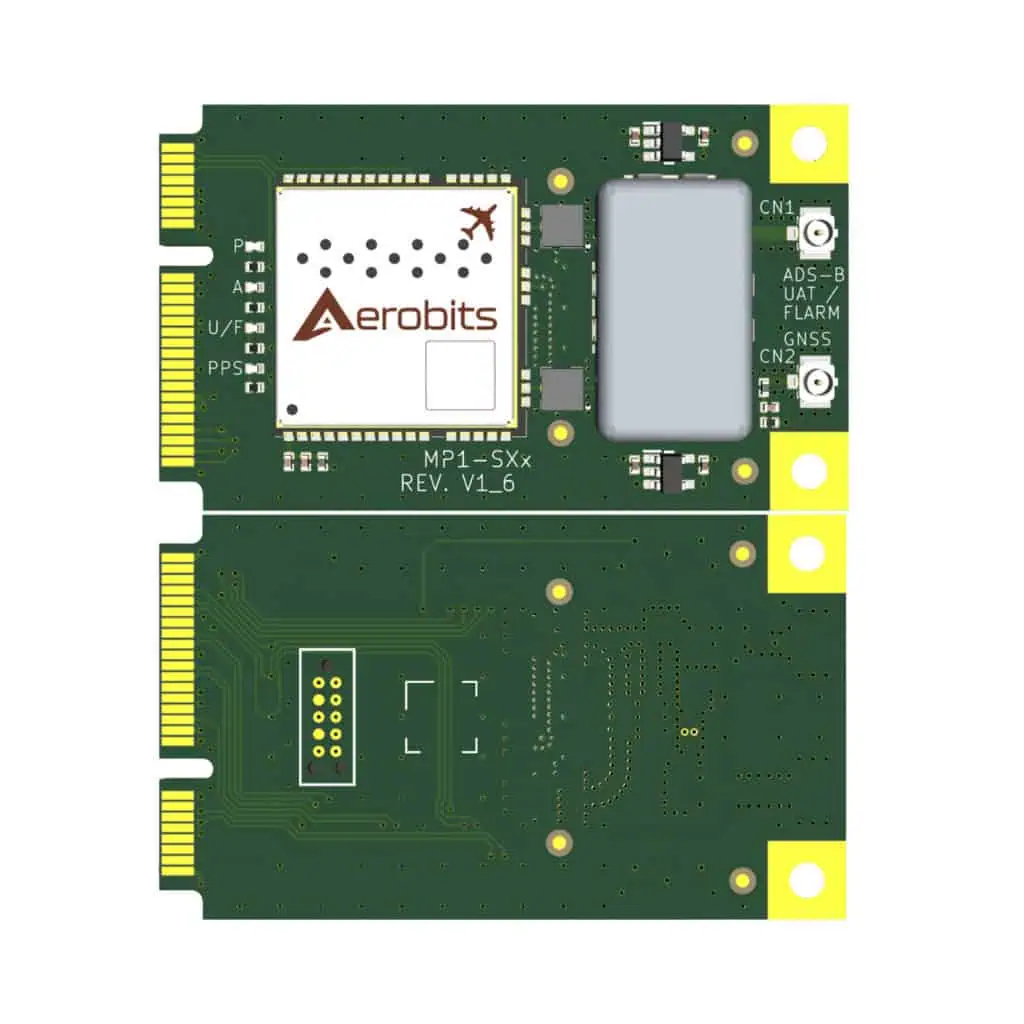
Miniature ADS-B Technology (Transceivers/Receivers) and Drone Tracking Transponders for sUAS & UTM/U-Space
If you design, build or supply GNSS Receivers, create a profile to showcase your capabilities on this page
Products
GNSS Receivers and Modules for Drones, UGVs, and Autonomous Systems
In this guide
- Understanding GNSS Receivers
- Applications in Unmanned Systems
- Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs)
- Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs)
- Unmanned Surface Vehicles (USVs)
- Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs)
- Robotics and Industrial Automation
- Defense and Tactical Systems
- Space and Near-Space Platforms
- Public Safety and Search & Rescue (SAR)
- Environmental Monitoring
- Law Enforcement and Forensics
- Commercial Survey and Inspection
- Types and Configurations
- Performance Considerations
- Standards and Protocols
- Comparative Technologies
- Emerging Trends and Capabilities
Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receivers, including integrated GPS modules and chipsets, are foundational technologies in the operation of unmanned systems.
From UAVs to autonomous ground vehicles, GNSS receivers provide the critical geospatial data for navigation, timing, and control. These devices range from compact modules for size-constrained platforms to high-precision RTK receivers in surveying and tactical operations. Supporting standards like NMEA 0183 and NMEA 2000, modern GNSS hardware is designed for compatibility, performance, and resilience in environments where continuous signal access and accuracy are paramount.
Understanding GNSS Receivers
GNSS receivers process signals from multiple satellite constellations such as GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou to determine position, velocity, and time. These receivers decode timing signals to calculate a device’s precise location, vital for unmanned platforms requiring accurate autonomous navigation.
While traditional GPS receivers focus on one constellation, modern GNSS receivers use multi-constellation and multi-frequency signals to enhance redundancy and improve accuracy under challenging conditions such as urban canyons, dense forests, or GNSS-contested environments.
Applications in Unmanned Systems
GNSS receivers are pivotal in various unmanned and autonomous platforms across air, land, sea, and subsea domains. Their integration ensures precise navigation, system coordination, and operational reliability. In particular, UAV GNSS systems and GNSS for drones are critical for enabling autonomous aerial operations with high positional accuracy and stability. As unmanned systems evolve in complexity, the demand for resilient, high-accuracy GNSS hardware continues to grow.
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs)
UAVs rely on GNSS receivers for waypoint navigation, geofencing, altitude hold, and return-to-home (RTH) functions. UAV GNSS modules are especially important in flight control systems that support stable, autonomous operation. Precision agriculture UAVs use RTK GNSS to map crop health and apply treatments with sub-meter accuracy. Tactical drones utilize military-grade GNSS with anti-jamming features for mission-critical navigation in contested airspace.
Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs)
Ground robots use GNSS for autonomous pathfinding, route optimization, and coordinated convoy operations. Survey-grade UGVs equipped with RTK receivers can perform topographic and infrastructure mapping in large or remote areas. In defense, armored UGVs integrate GNSS with IMUs to navigate in GPS-degraded environments.
Unmanned Surface Vehicles (USVs)
USVs rely on GNSS to follow preprogrammed maritime routes, perform bathymetric surveys, and monitor marine environments. High-precision GNSS receivers enable these vessels to maintain steady trajectories despite wind, waves, and current-induced drift. In naval applications, GNSS-equipped USVs can patrol harbors or act as decoys.
Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs)
While GNSS signals do not penetrate water, UUVs use GNSS at the surface to acquire a fix before submerging. This position is then carried forward using inertial navigation. Some hybrid systems allow GNSS/INS recalibration when briefly surfaced, maintaining positional integrity over extended missions.
Robotics and Industrial Automation
Warehouse and logistics robots integrate GNSS with LIDAR and vision systems for indoor-outdoor navigation. Outdoor service robots for mining or agriculture use GNSS to maintain lane guidance, field coverage, or geofencing boundaries. Autonomous delivery robots use GPS/GNSS receivers for route tracking and arrival coordination.
Defense and Tactical Systems
In military systems, GNSS receivers provide encrypted position and timing data for secure operations. These receivers may support SAASM or M-Code for access to secure satellite signals. Applications include missile guidance, command and control (C2) synchronization, battlefield asset tracking, and personnel navigation under low-visibility or GNSS-degraded conditions.
Space and Near-Space Platforms
High-altitude balloons and small satellites (CubeSats) use GNSS receivers to maintain positional awareness and timing during scientific or communications missions. Specialized GNSS modules are optimized for high-velocity dynamics and ionospheric conditions found at the edge of space.
Public Safety and Search & Rescue (SAR)
GNSS-equipped drones and UGVs assist in SAR missions by mapping disaster areas, locating signals from personal locator beacons (PLBs), and providing situational awareness in environments inaccessible to ground teams.
Environmental Monitoring
GNSS receivers support unmanned systems monitoring climate conditions, wildlife movements, and natural resources. Drones equipped with high-accuracy GNSS collect geotagged data for environmental modeling and change detection.
Law Enforcement and Forensics
Forensic teams deploy GNSS-enabled unmanned platforms to map crime scenes or accident locations with centimeter-level accuracy, preserving evidence integrity and supporting digital reconstruction efforts.
Commercial Survey and Inspection
GNSS receivers enable autonomous aerial and terrestrial surveys of pipelines, power lines, construction sites, and transportation corridors. These receivers support high-frequency position updates and integrate with RTK correction services for precise mapping.
Types and Configurations
GNSS receivers are available in several configurations:
- GNSS Chips and Chipsets: Integrated circuits for custom embedded systems with compact form factors
- GNSS Modules: Ready-to-deploy packages combining antennas, interfaces, and signal processing components
- Standalone GNSS Receivers: Units with onboard processing, external antennas, and ruggedized housings for field deployment
- RTK GNSS Receivers: Real-Time Kinematic receivers providing centimeter-level accuracy using differential signal correction
- Dual-Antenna Receivers: Used for heading and orientation in mobile platforms
- GNSS/INS Systems: Integrated inertial navigation with IMUs for continuity in GNSS-denied areas
Performance Considerations
Key performance factors for GNSS receivers include:
- Accuracy: High-precision receivers offer sub-meter to centimeter-level positioning
- Sensitivity: Determines the ability to acquire signals in low-SNR or obstructed environments
- Update Rate: High update rates (10 Hz or more) support real-time navigation
- Interfaces: Common outputs include NMEA 0183, NMEA 2000, USB, serial, and Ethernet
- Time Synchronization: Some units include disciplined oscillators for precise timing
- Environmental Resilience: Industrial and military-grade receivers are built for extreme temperature, vibration, and moisture conditions
Standards and Protocols
GNSS receiver technologies are governed and supported by a range of international standards:
- NMEA 0183 / NMEA 2000: Communication protocols for marine and mobile GNSS integration
- MIL-STD-810 / MIL-STD-461: Environmental and EMI compliance for military-grade receivers
- RTCM: Differential correction messages for RTK systems
- SAASM / M-Code: Secure military-grade positioning protocols for authorized users
Comparative Technologies
When selecting GNSS receivers, users may compare:
- GNSS vs GPS: GNSS includes multiple satellite systems, while GPS refers specifically to the U.S. constellation
- RTK vs SBAS: RTK provides higher accuracy using base stations; SBAS offers augmentation over a wider area
- Single vs Multi-Frequency: Multi-frequency receivers mitigate multipath and improve convergence times
- Integrated vs Modular Receivers: Integrated solutions simplify deployment; modular options offer flexibility
GNSS for drones typically favors lightweight, integrated modules to reduce payload weight while maintaining high-performance navigation accuracy.
Emerging Trends and Capabilities
Technological developments in GNSS receivers include:
- Miniaturization: Chipsets enabling GNSS integration into compact UAVs and robotics
- Anti-Jamming and Anti-Spoofing: Protection for mission-critical navigation
- Multi-Constellation Tracking: Enhanced availability and reliability
- GNSS-INS Fusion: Seamless navigation in GNSS-denied environments
- Software-Defined GNSS Receivers: Flexibility for algorithm updates and signal simulation





























































